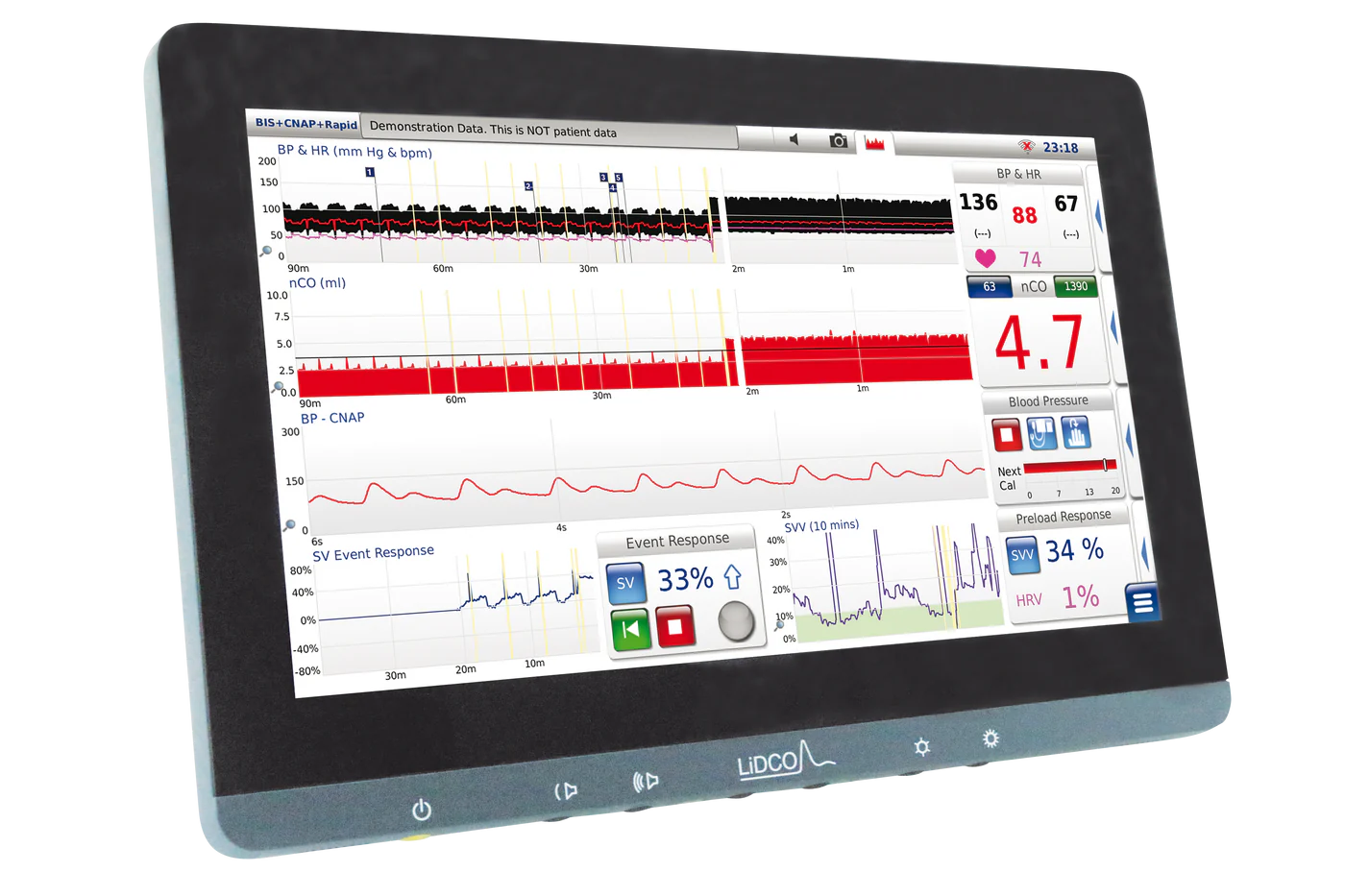
The use of lithium for calibration in LiDCO (Lithium Dilution Cardiac Output) monitoring systems is based on its properties and suitability for the measurement technique employed by the device. Here’s why lithium is commonly used for calibration in LiDCO machines:
- Biocompatibility: Lithium chloride, the compound typically used in LiDCO systems, is considered safe for use in humans in small quantities. It is well-tolerated and does not usually cause adverse reactions when administered in controlled amounts.
- High solubility: Lithium chloride has high solubility in water, allowing for the creation of a precise and consistent concentration solution for calibration purposes. This solubility ensures accurate dilution measurements during the calibration process.
- Ionic properties: Lithium is a monovalent cation, meaning it carries a single positive charge. This property allows it to be easily detected by sensors in the LiDCO system, facilitating accurate measurement of its concentration in the bloodstream.
- Stability: Lithium chloride solutions are relatively stable, which is important for maintaining the consistency and reliability of calibration standards over time. This stability ensures that calibration measurements remain accurate and consistent during repeated use of the LiDCO system.
- Low interference: Lithium chloride solutions typically do not interfere with other substances or processes in the bloodstream, minimizing the likelihood of false readings or inaccuracies during calibration and measurement.
Overall, the choice of lithium for calibration in LiDCO monitoring systems is based on its combination of biocompatibility, solubility, ionic properties, stability, and low interference, which make it well-suited for the precise and accurate measurement techniques utilized by the device.