In the UK, the diagnosis of brain stem death is carried out with strict adherence to guidelines established by professional bodies, such as the Academy of Royal Medical Colleges. During brain stem death testing, several reflexes are assessed to determine the absence of brain stem function. These reflexes are involuntary responses controlled by the brainstem, and their absence indicates a severe lack of brain activity.
Two qualified doctors
Two qualified doctors: Once the preconditions are met, the diagnosis must be made by two separate doctors, at least one of whom is a senior doctor (consultant) and neither of whom can be involved with the hospital’s transplant team. This ensures objectivity and avoids conflicts of interest.
The following reflexes and responses are tested:
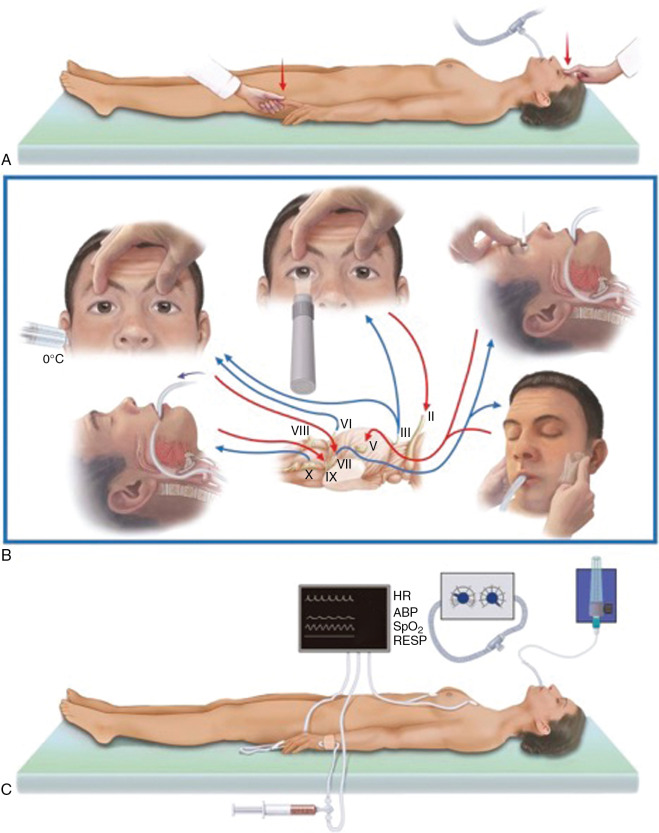
- Pupillary Light Reflex
- Method: Shine a bright light into each eye.
- Normal Response: Pupils constrict.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: Pupils remain fixed and dilated (no response to light).
- Corneal Reflex
- Method: Touch the cornea with a piece of sterile cotton wool or gauze.
- Normal Response: Blinking or eye movement.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: No blinking or eye movement.
- Oculocephalic Reflex (Doll’s Eye Reflex)
- Method: Rapidly turn the patient’s head from side to side.
- Normal Response: Eyes move in the opposite direction of head movement.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: Eyes remain fixed in position (no movement).
- Oculovestibular Reflex (Cold Caloric Test)
- Method: Elevate the head to 30 degrees, irrigate the ear canal with ice-cold water.
- Normal Response: Eyes deviate towards the irrigated ear.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: No eye movement.
- Pain Response (Supraorbital Pressure):
- Method: Apply firm pressure to the supraorbital ridge (area above the eye socket).
- Normal Response: The patient shows a facial grimace or other movement in response to the pressure.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: No facial grimace or movement is observed
- Gag Reflex
- Method: Stimulate the back of the throat with a tongue depressor.
- Normal Response: Gagging or throat movement.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: No gagging or throat movement.
- Cough Reflex
- Method: Suction the trachea or bronchial tree.
- Normal Response: Coughing.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: No coughing.
- Apnea Test
- Purpose: Assesses the brain stem’s control over spontaneous breathing.
- Method: Disconnect the ventilator while providing 100% oxygen through a catheter placed at the level of the carina. Monitor for spontaneous breathing movements.
- Brain Stem Death Indicator: No respiratory movements and an increase in PaCO2 above a critical threshold (usually > 6.65 kPa or an increase of 3.33 kPa from baseline).
Documentation and Confirmation
- Independent Testing: Two doctors, each with more than five years of experience, independently perform and document the tests.
- Repetition: The tests are repeated after an interval, ensuring consistency in the findings.
- Documentation: All findings, including the absence of brain stem reflexes and the results of the apnea test, are thoroughly documented.
- Consultation: The findings are discussed with the patient’s family, explaining the diagnosis and the implications of brain stem death.
Conclusion
The determination of brain stem death in the UK is a rigorous and systematic process designed to ensure accuracy and reliability. It involves meeting specific preconditions, performing a series of clinical tests to confirm the absence of brain stem function, and thorough documentation by experienced clinicians. This careful approach is essential for making critical decisions regarding the cessation of life support and organ donation.
