Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain Stem
The brainstem is the lower part of the brain that connects the cerebrum (the large upper part of the brain) to the spinal cord. It’s a vital part of the nervous system that is responsible for many automatic functions, including:
- Breathing
- Heart rate
- Blood pressure
- Digestion
- Swallowing
- Sensory and motor function (e.g., relaying messages between the brain and the body)
- Sleep and wake cycles
- Consciousness
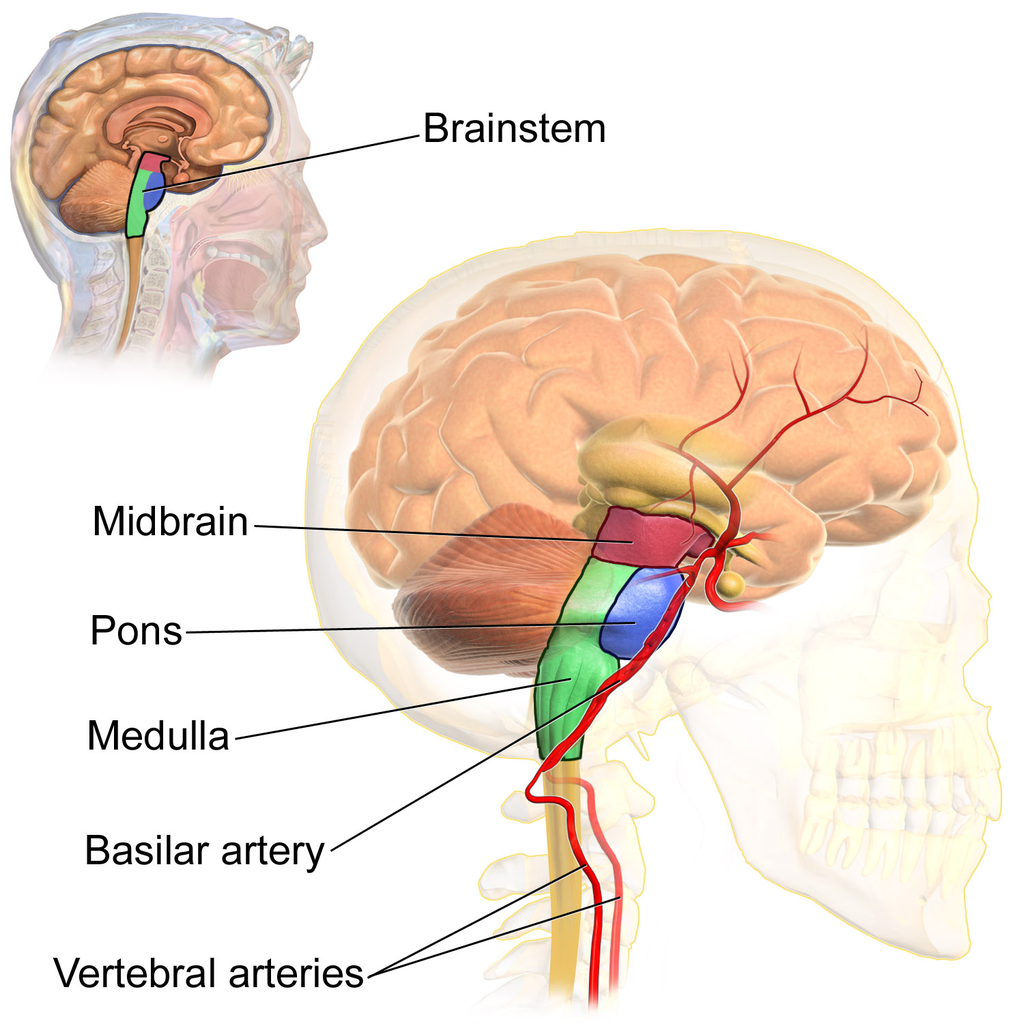
The brainstem is made up of three main parts:
- Midbrain:The midbrain is the uppermost part of the brainstem. It’s involved in vision, hearing, movement, and alertness.
- Pons:The pons is located below the midbrain. It’s involved in sleep, alertness, facial expressions, swallowing, chewing, hearing, and balance.
- Medulla oblongata:The medulla oblongata is the lowermost part of the brainstem. It’s responsible for many essential functions, including breathing, heart rate, blood pressure, digestion, swallowing, and reflexes.
Brain Stem location and functions
- Midbrain (Mesencephalon)
- Location: The uppermost part of the brain stem, located between the pons and the diencephalon (thalamus and hypothalamus).
- Functions:
- Visual and Auditory Reflexes: Mediated by the superior and inferior colliculi.
- Motor Control: Through the red nucleus and substantia nigra.
- Regulation of Arousal and Alertness: Via the reticular formation.
- Pons
- Location: The middle part of the brain stem, located between the midbrain and the medulla oblongata.
- Functions:
- Relay of Motor Information: From the cerebral cortex to the cerebellum.
- Regulation of Breathing: Through the pneumotaxic and apneustic centers.
- Facial Sensation and Movement: Via cranial nerve nuclei.
- Medulla Oblongata
- Location: The lower part of the brain stem, continuous with the spinal cord.
- Functions:
- Autonomic Functions: Regulation of heart rate, blood pressure, and respiratory rate.
- Reflex Centers: For coughing, vomiting, sneezing, and swallowing.
- Relay of Sensory and Motor Information: Between the brain and the spinal cord.
summery
The brainstem is a complex and important part of the brain. Damage to the brainstem can be very serious and can lead to coma or even death
.
