Comparison of Cardiac Muscle and Skeletal Muscle
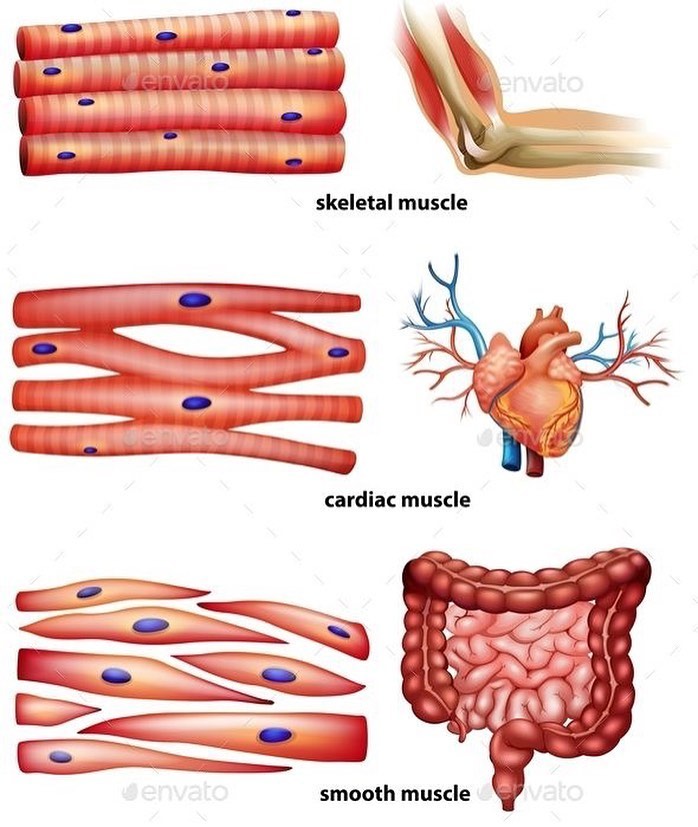
| Feature | Cardiac Muscle | Skeletal Muscle |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Involuntary, single nucleus, abundant mitochondria | Voluntary, multi-nucleated, fewer mitochondria |
| Function. | Pumps blood | Movement of bones and joints |
| Control | Involuntary, self-excitable | Voluntary |
| Contraction | Rhythmic, sustained | Voluntary, short bursts |
| Blood Supply | Dedicated network (coronary arteries) | Increases with activity |
| Regeneration | Limited | Higher capacity |
Additional Details
1. Structure:
- Cardiac Muscle:
- Involuntary: Cells are interconnected by structures called intercalated discs, forming a functional syncytium.
- Striated: Organised arrangement of contractile proteins (actin and myosin) giving a striped appearance.
- Single nucleus per cell: Located centrally.
- Abundant mitochondria: Provides energy for sustained contraction.
- Skeletal Muscle:
- Voluntary: Controlled consciously.
- Striated: Similar to cardiac muscle.
- Multi-nucleated: Each cell contains multiple nuclei located peripherally.
- Fewer mitochondria: Relies on short bursts of energy.
2. Function:
- Cardiac Muscle:
- Contraction: Pumps blood throughout the body.
- Rhythmic and involuntary: Initiated by pacemaker cells and maintains a steady rhythm.
- Cannot fatigue: Designed for continuous work.
- Skeletal Muscle:
- Contraction: Enables movement of bones and joints.
- Voluntary and controlled: Allows conscious control of movement.
- Can fatigue: Requires periods of rest for recovery.
3. Control:
- Cardiac Muscle:
- Involuntary: Controlled by the autonomic nervous system and hormones.
- Self-excitable: Pacemaker cells initiate the electrical impulses.
- Skeletal Muscle:
- Voluntary: Controlled by the nervous system through motor neurons.
- Not self-excitable: Requires stimulation from the nervous system to contract.
Additional Differences:
- Blood Supply: Cardiac muscle has its own dedicated blood supply network (coronary arteries) to meet its high energy demands. Skeletal muscle blood flow increases with activity to deliver oxygen and nutrients.
- Regeneration: Cardiac muscle has limited regenerative capacity, while skeletal muscle has a higher capacity for repair and regeneration.
