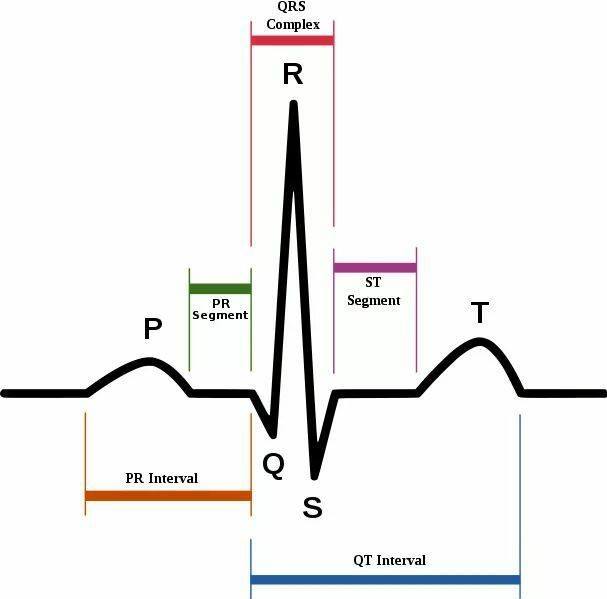
Sinus rhythm is the normal regular rhythm of the heart where the electrical impulses originate from the sinoatrial (SA) node. Confirming sinus rhythm on an electrocardiogram (ECG) involves checking several key factors:
Factors Confirming Sinus Rhythm on an ECG
- P Wave Origin:
- Generation from SA Node: The P wave must originate from the sinoatrial (SA) node, which is the natural pacemaker of the heart. This confirms that the rhythm is sinus in nature.
2. P Waves:
- Presence: There should be a P wave before every QRS complex.
- Morphology: The P waves should be of normal shape and size.
- Direction: In leads I, II, and aVF, P waves should be upright (positive).
- Negative P Waves: P waves should be negative in lead aVR.
3. PR Interval:
- Duration: The PR interval (beginning of the P wave to the beginning of the QRS complex) should be consistent and measure between 120 to 200 milliseconds (0.12 to 0.20 seconds).
4. QRS Complex:
- Association: Each P wave should be followed by a QRS complex.
- Duration: The QRS duration should be within normal limits (less than 120 milliseconds or 0.12 seconds).
5. Regularity:
- Rhythm: The intervals between consecutive R waves (R-R intervals) should be consistent, indicating a regular rhythm.
6. Heart Rate:
- Rate: The heart rate should typically be between 60 and 100 beats per minute for a normal sinus rhythm at rest.
7. P Wave Axis:
- Axis: The normal P wave axis should be between 0° and +75°.
Additional Considerations
- Respiratory Sinus Arrhythmia: It’s normal for there to be a slight variation in the heart rate with respiration. This is seen more in younger individuals and typically signifies a healthy heart.
- Sinus Bradycardia: Sinus rhythm with a heart rate less than 60 beats per minute.
- Sinus Tachycardia: Sinus rhythm with a heart rate more than 100 beats per minute.
- Sinus Arrhythmia: A normal variation in sinus rhythm where the heart rate varies with breathing (common in young, healthy individuals).
Summary Checklist for Confirming Sinus Rhythm
- P Wave Origin:
- Generated by the SA node, confirming sinus rhythm.
2. P Waves:
- Positive in leads I, II, aVF
- Negative in lead aVR
- One P wave before each QRS complex
3. PR Interval:
- Duration: 120-200 milliseconds
- Consistent interval
4. QRS Complex:
- Follow each P wave
- Duration: Less than 120 milliseconds
5. Regularity:
- Regular R-R intervals
6. Heart Rate:
- 60-100 beats per minute at rest
By checking these factors, you can confirm whether a patient has a sinus rhythm on their ECG. If any of these factors are abnormal, it might suggest an arrhythmia or another type of cardiac condition that requires further investigation.
